Six Sigma vs Lean: What's the Difference?
Six Sigma and Lean are two popular methodologies used in business management in order to improve processes, increase efficiency, and reduce waste. While both methods aim to improve the quality and productivity of an organization, there are some significant differences between the two. Yet, before talking about differences I would like to make a brief review of Six Sigma and Lean.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a quality management methodology used by companies to improve business processes, reduce defects, and increase efficiency. It was first developed by Motorola in the 1980s, and later popularized by General Electric.
The core principle of Six Sigma is to identify and eliminate the causes of defects (errors or mistakes) in a process, by using statistical methods and tools. The goal is to achieve a level of quality where the probability of defects occurring is extremely low (less than 3.4 defects per million opportunities).
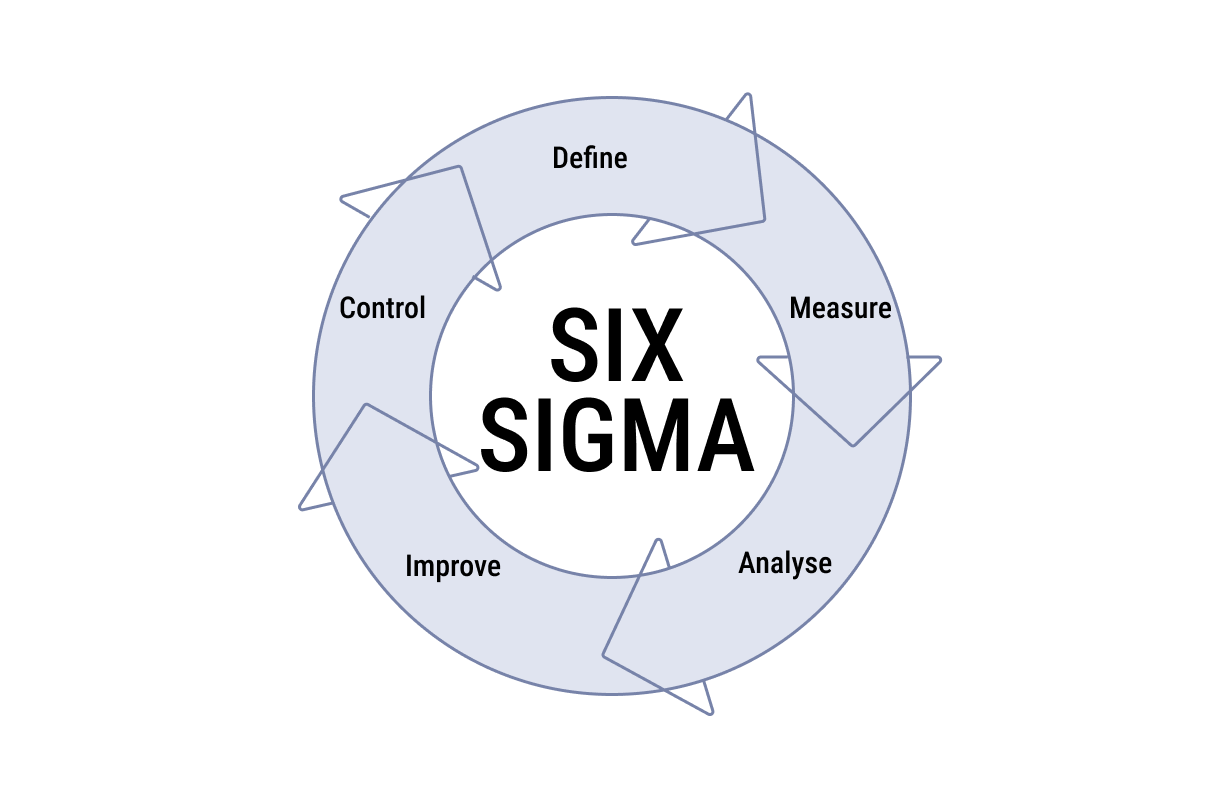
The methodology is based on a structured approach called DMAIC, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. This process involves defining the problem or issue, measuring the current performance, analyzing the data to identify the root causes of the problem, improving the process by implementing solutions, and controlling the new process to ensure that it is sustainable and continuously improving.
Six Sigma has been widely adopted in many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors, as a way to improve quality and reduce costs. It has also been used to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, by delivering products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
What is Lean?
Lean is a methodology for process improvement that aims to eliminate waste, increase efficiency, and maximize customer value. It was first developed by Toyota in the 1950s and is also known as the Toyota Production System.
The core principle of Lean is to focus on the flow of work and the value that is added at each step of the process. The methodology emphasizes the importance of identifying and eliminating any activity that does not add value to the customer, such as waiting, overproduction, unnecessary movement, over processing, defects, and unused talent.
The Lean approach is based on several key principles, including continuous improvement, respect for people, just-in-time production, and visual management. It is often implemented through a structured approach called the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, which involves planning the improvement, implementing it, checking the results, and acting to sustain the improvement.
Lean has been applied in many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, construction, and service sectors, to improve quality, reduce lead time, increase productivity, and lower costs. It has also been used to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by delivering products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
The Differences Between Lean Six Sigma and Six Sigma
The key differences between Six Sigma and Lean are based on focus, tools, goals, approaches, etc. Let’s start from focus. As you know, Six Sigma aims to reduce defects and improve the quality of products or services by focusing on identifying and removing the root causes of errors, defects, or variations in a process. On the other hand, Lean focuses on eliminating waste, which includes any activity that does not add value to the end product or service.
And what about approach? Six Sigma uses a data-driven approach to identify and solve problems, often involving statistical analysis and measurement tools. In contrast, Lean relies on identifying and eliminating waste through continuous improvement and value stream mapping.
The scope also matters. Six Sigma can be applied to a wide range of industries and processes, including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. In contrast, Lean was initially developed for the manufacturing industry but has been adapted to various industries, including healthcare, service, and government.
Tools may vary. When Six Sigma utilizes tools such as statistical process control, design of experiments, and root cause analysis to identify and solve problems, Lean, in contrast, uses tools such as value stream mapping, Kanban, and 5S to eliminate waste and optimize processes.
The goals differ as a rule. Six Sigma aims to reduce defects to a minimum level, with a target of 3.4 defects per million opportunities. In contrast, Lean focuses on maximizing customer value by eliminating waste and creating a continuous flow of products or services.
In summary, Six Sigma focuses on reducing errors and improving quality through data-driven analysis and problem-solving techniques, while Lean aims to eliminate waste and optimize processes through continuous improvement and value stream mapping. Both methodologies are complementary and can be used together to achieve process excellence and customer satisfaction.
Lean vs. Six Sigma: Which Methodology is Better?
Both Lean and Six Sigma are highly effective methodologies for process improvement, and each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing between the two depends on the specific needs of the organization, the nature of the problem being addressed, and the goals of the improvement initiative.
Lean is best suited for organizations that are seeking to improve the flow of work, eliminate waste, and increase efficiency. It is particularly effective in manufacturing and service sectors where there is a high volume of repetitive tasks. Lean emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement and empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste in the process. It is highly flexible and can be easily adapted to different industries and situations.
Six Sigma, on the other hand, is best suited for organizations that are seeking to reduce defects, improve quality, and increase customer satisfaction. It is particularly effective in industries where quality is critical, such as healthcare and finance. Six Sigma uses statistical analysis and tools to identify and eliminate the root causes of defects in the process. It emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making and requires specialized training and expertise.
In some cases, organizations may choose to use both Lean and Six Sigma together, as they complement each other and address different aspects of process improvement. This is often referred to as Lean Six Sigma, and it combines the focus on eliminating waste and increasing efficiency of Lean with the data-driven approach to quality improvement of Six Sigma. Ultimately, the choice between Lean and Six Sigma, or a combination of both, depends on the specific needs and goals of the organization.
What is known about the Differences Between Lean vs Six Sigma in Project Management?
In project management, Lean and Six Sigma have different approaches and tools that can be used to achieve similar objectives. Here are some of the key differences between Lean and Six Sigma in project management:
- Lean focuses on eliminating waste and increasing efficiency, while Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and improving quality.
- Lean can be applied to any aspect of the project, including planning, design, development, testing, and delivery, while Six Sigma is typically used in the quality control and improvement phases of the project.
- Lean tools include value stream mapping, 5S workplace organization, Kanban, and Kaizen events. Six Sigma tools include statistical analysis, control charts, process mapping, and root cause analysis.
- Lean is typically implemented through the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, while Six Sigma uses the DMAIC (Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control) cycle.
- Lean teams are often cross-functional and include representatives from different departments, while Six Sigma teams are typically led by a Six Sigma Black Belt and include subject matter experts and stakeholders.
- Lean training is often focused on empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste in the process, while Six Sigma training is focused on statistical analysis and problem-solving techniques.
In project management, organizations may choose to use either Lean or Six Sigma, or a combination of both, depending on the specific goals of the project and the nature of the problem being addressed. The choice between the two methodologies depends on the type of project, the level of quality required, and the desired outcome.

Lean project management
Lean project management is an approach to project management that emphasizes the elimination of waste, increasing efficiency, and maximizing customer value. It applies the principles of Lean manufacturing to project management, with the goal of delivering projects on time, within budget, and with high quality.
The core principle of Lean project management is to focus on the value added at each step of the project, and to eliminate any activity that does not add value to the customer. The methodology emphasizes continuous improvement, visual management, and teamwork to streamline the project process and increase efficiency.
In Lean project management, the focus is on the flow of work, rather than the individual tasks or activities. This means that the project team works together to identify and eliminate waste in the process, and to continuously improve the process through regular review and feedback.
The Lean project management process typically involves 5 steps:
- Define the project goals and objectives, and identify the customer and their requirements.
- Map the value stream, identify the current process, and identify any areas of waste.
- Develop a plan to eliminate waste and improve efficiency, and implement changes to the process.
- Monitor the process and measure performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Continuously improve the process through ongoing review and feedback.
The Lean project management approach has been successfully applied in many industries, including construction, healthcare, software development, and engineering. It has been shown to increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction by delivering projects that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Six Sigma project management
Six Sigma project management is an approach to project management that emphasizes the use of statistical tools and data analysis to improve the quality and efficiency of the project. It applies the principles of Six Sigma to project management, with the goal of delivering projects that meet or exceed customer expectations, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
The core principle of Six Sigma project management is to identify and eliminate defects in the process, using statistical analysis and problem-solving techniques. The methodology emphasizes a data-driven approach to decision-making, with the goal of minimizing variability and achieving a high level of process control.
In Six Sigma project management, the process typically follows the DMAIC (Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control) methodology:
- Define the project goals and objectives, and identify the customer and their requirements.
- Measure the current process, identify the critical-to-quality (CTQ) factors, and establish a baseline performance level.
- Analyze the data, identify the root causes of defects, and develop solutions to address them.
- Improve the process by implementing the solutions, and verifying the effectiveness of the changes.
- Control the process by monitoring performance, establishing control plans, and implementing corrective actions as needed.
The Six Sigma project management approach has been successfully applied in many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service industries. It has been shown to improve quality, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction by delivering projects that meet or exceed customer expectations, and are completed on time and within budget.
Which to do first? Lean or Six Sigma?
Whether to implement Lean or Six Sigma first depends on the specific needs and goals of the organization. Both methodologies can be implemented together or separately, and the order of implementation will depend on the particular circumstances.
If an organization is looking to streamline its processes, reduce waste, and increase efficiency, then Lean may be the best place to start. Lean can help organizations to identify and eliminate waste in their processes, and to improve efficiency and quality by focusing on value-added activities.
On the other hand, if an organization is experiencing quality issues, defects, or variations in its processes, then Six Sigma may be the best place to start. Six Sigma can help organizations to identify the root causes of defects and to develop solutions to eliminate them, resulting in improved quality, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
Ultimately, the decision to implement Lean or Six Sigma first should be based on an assessment of the organization's current state and future goals, as well as the resources available to implement the methodologies. Many organizations choose to implement both methodologies together in a complementary manner, as they can work hand in hand to achieve the same objectives of increased efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.